Global Terrestrial Reference Frames
The International Terrestrial Reference System (ITRS) is the fundamental Earth-fixed coordinate system and provides the framework for referencing geodetic and astronomical observations. A highly accurate realization of the coordinate system, the so-called Reference Frame, is of paramount importance for various socially relevant applications including navigation and positioning, and forms the backbone for scientific exploration of the Earth system by providing the reference for monitoring dynamic processes and effects of climate change, such as ice melt or sea level rise. The ITRS is realized by positions and velocities of more than 1800 globally distributed geodetic observing stations. Station positions and velocities are derived from a combination of the geodetic space techniques VLBI, SLR, GNSS, and DORIS. Each of the techniques offers individual strengths in terms of determining geodetic parameters - in particular the parameters of the geodetic datum (origin, orientation, scale) of the reference frame.
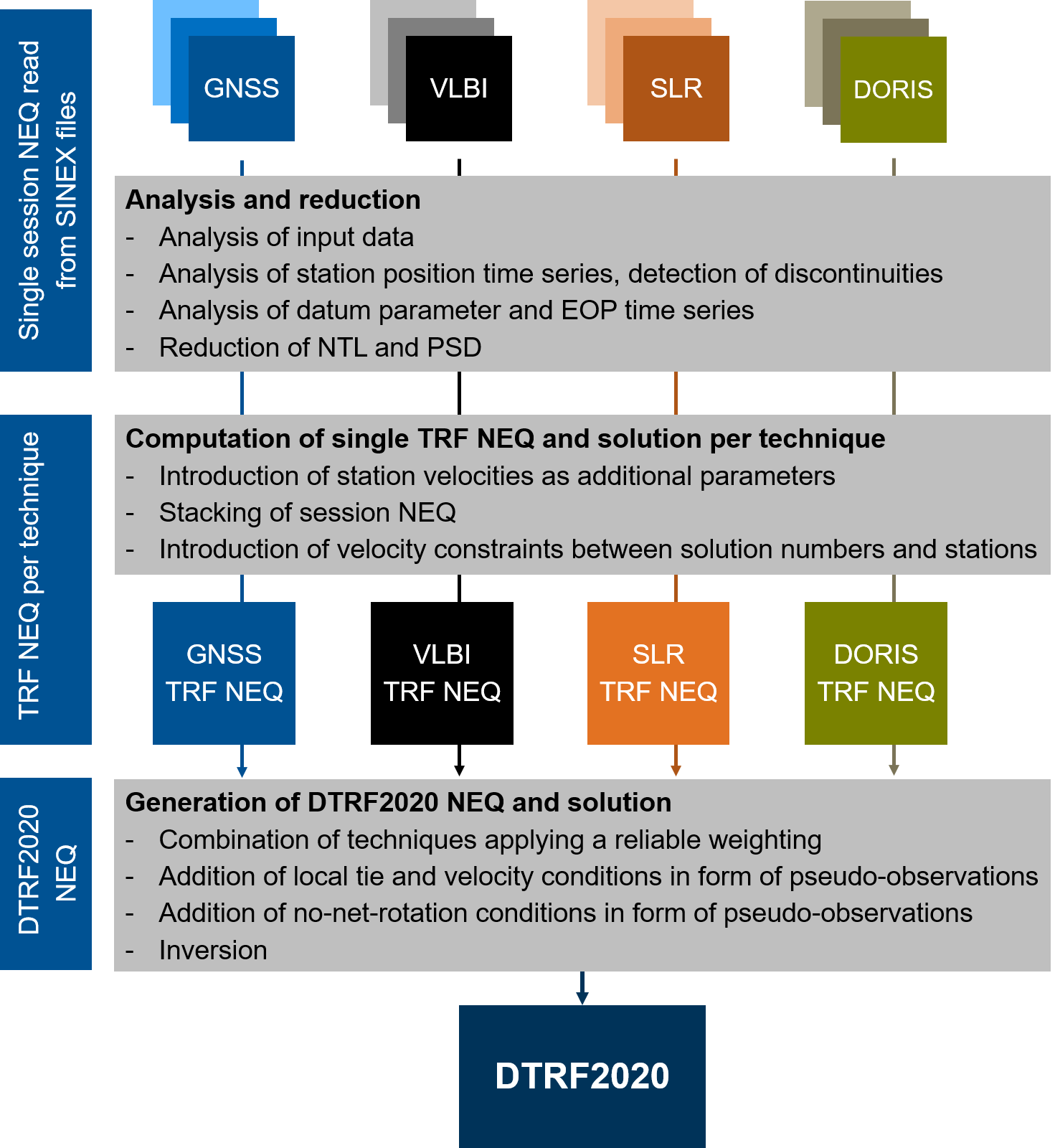
The calculation of the reference frame at DGFI-TUM follows a 2-step approach: First, time series of normal equation (NEQ) systems of the individual techniques are analyzed and combined into one normal equation system per technique (intra-technique combination). Second, the NEQ systems of the different techniques are combined to the reference frame (inter-technique combination).
In its role as an ITRS Combination Centre within the International Earth Rotation and Reference Systems Service (IERS), DGFI-TUM has taken responsibility for the continuous realization of the ITRS with best possible accuracy and long-term stability. DGFI-TUM's latest realization of the ITRS is the DTRF2020.
The main goal of DGFI-TUM's research activities in this context is to further develop the global reference frame by improving its accuracy, stability, timeliness and consistency. In particular, DGFI-TUM investigates the potential and optimal strategy for the consistent realization of the terrestrial and celestial reference system according to Resolution 3 (2011) of the International Union of Geodesy and Geophysics (IUGG) as well as the integration of geometry and gravity in the sense of GGOS.
Related projects (DFG, Research Unit "Clock Metrology")
- Application of time in closure as a novel strategy towards error-free space geodetic observations
- Novel clock technologies for combination on ground and in space: real data and simulation
Related data products
- International Terrestrial Reference System (ITRS): DGFI-TUM realization DTRF2020
- International Terrestrial Reference System (ITRS): DGFI-TUM realization DTRF2014
- International Terrestrial Reference System (ITRS): DGFI-TUM realization DTRF2008
Selected Publications
 (Open Access)
(Open Access)





Arcisstraße 21
80333 München